Lesson 71 – الدَّرْسُ الحادِي والسَّبْعونَ
The status - الْحَال
Introduction - مُقَدِّمَةٌ
- This is lesson seventy one of our free Arabic language course. This Arabic course with images and audios will help you learn Arabic.
- In the previous five lessons we learnt the five types of the Arabic objects (الْمَفاعِيل / al mafāξeel). We learnt that the objects are accusative dispensable nouns in the Arabic verbal sentence. All the five objects are related to the verb, and affected by it.
- In this lesson we will study another accusative noun in the Arabic verbal sentence, which is the status (الْحال / alħāl). Unlike the objects, the status is not related to the verb; rather it is related to another noun in the verbal sentence which is called the concerned noun. The concerned noun can be the doer (الفاعِل/alfāξil) as in the following sentence:
| Pictur | English | Arabic |
|
| Muhammad came walking (on foot) | /ĵā’a muħammadun māshiyan/
|
- The concerned noun can also be the direct object as follows:
| Pictur | English | Arabic |
|
| I saw the student happy | /ra’aytu aŧ ŧâliba saξīdan/ |
- In the above mentioned two examples we notice that the status (ماشِيًا - سَعِيدًا) is an accusative dispensable noun (supplement), which describes the aspect of the concerned noun in the occurrence of the verb.
- In this lesson we will learn the following topics In-Shā’-Allâh (God willing):
1- The definition of the status, with examples.
2- The conditions of the status, and of the concerned noun, to which the status is related. E.g. the status should be indefinite, and the concerned noun should be definite as in the following examples:
| Pictur | Concerned | Status | Example | |
| English | Arabic | |||
|
| The boy came hurrying | /ħađara al waladu musriξan/ | ||
|
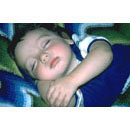
| The child sleeps unhappy | /yanāmu aŧ ŧiflu ħazīnan/ | ||
3- We will also learn the different types of the status, i.e. it can be a single noun, a sentence, or a quasi sentence (preposition + noun) as in the following examples:
|
Type Of status |
Single
| Arabic | /ĵā’a aŧ ŧâlibu bāsiman/ |
| English | The student came smiling | ||
| Arabic | /katabtu ad darsa | ||
| English | I wrote the lesson hurrying | ||
|
Sentence | Arabic | /ħađara aŧ ŧâlibu yabtasimu/ | |
| English | The student came smiling | ||
| Arabic | كَتَبْتُ الدَّرْسَ وَأنا أُسْرِعُ /katabtu ad darsa wa ana usriξu/ | ||
| English | I wrote the lesson while I was hurrying | ||
|
Quasi sentence | Arabic | جاءَ مُحَمَّدٌ فِي وَجْهٍ بَشُوشٍ /ĵā’a muħammadun fī waĵhin bashūshin/ | |
| English | Muhammad came bright-faced | ||
| Arabic | كَتَبْتُ الدَّرْسَ فِي عَجَلَةٍ /katabtu ad darsa fī ξaĵalatin/ | ||
| English | I wrote the lesson in hurry
|
4- We will also learn about the /wāw/ of the status, which comes in the beginning of the status sentence.